What are the differences between microbial, animal cell, and plant cell reactors?

Microbial cells: Microbial cells are relatively small, typically 1-5 μ m for bacteria and slightly larger for fungi. Having cell walls or no cellular structures (such as viruses), it has strong adaptability to the environment and can survive in various harsh environments.
Animal cells: Animal cells do not have cell walls, and their diameter is generally between 10-100 μ m. They are relatively fragile, sensitive to shear forces, and susceptible to mechanical damage.
Plant cells: Plant cells have cell walls and are larger in size than microbial cells, typically ranging from 10-200 μ m. The tolerance to shear force is between that of microbial cells and animal cells.

Nutritional requirements
Microbial cells have relatively simple nutritional requirements and can utilize various carbon and nitrogen sources to grow in relatively simple culture media. Escherichia coli can grow in a medium containing only glucose, inorganic salts, and nitrogen sources.
Animal cells: The nutritional requirements are very demanding. In addition to basic amino acids, vitamins, glucose, etc., complex components such as serum need to be added to provide growth factors and other substances.
Plant cells have simpler nutritional requirements than animal cells, generally requiring carbon sources such as inorganic salts and sucrose, plant growth hormones, etc., but usually do not require serum.
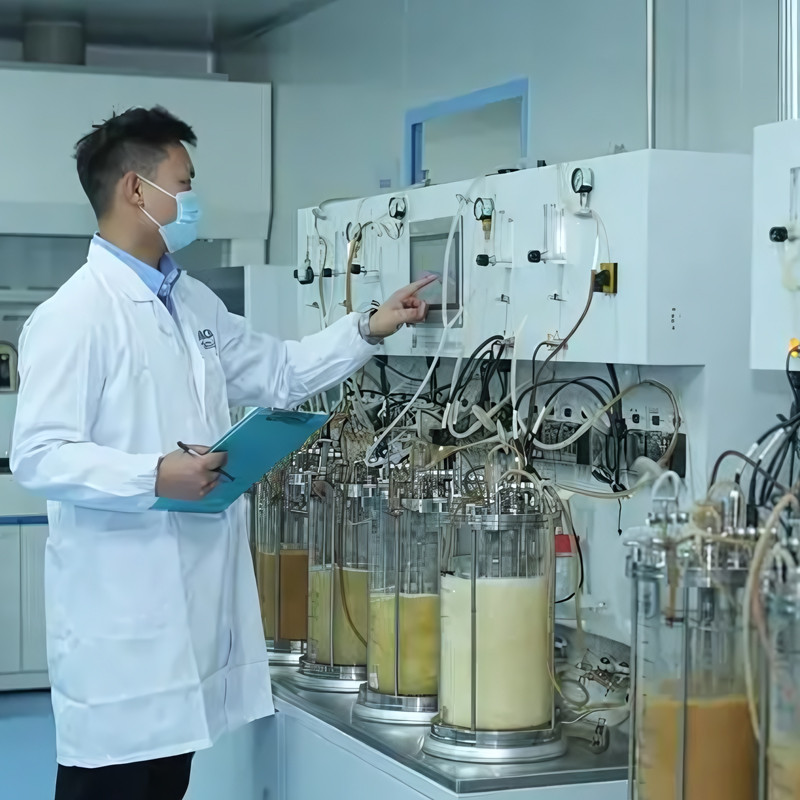

Characteristics of reactor design
Microbial reactors: typically have a large operating range and strong aeration and agitation capabilities to meet the rapid growth and metabolism of microorganisms for the mixing of oxygen and nutrients. Universal fermentation tanks have a large aspect ratio and are equipped with powerful stirring systems and ventilation devices.
Animal cell reactor: The focus is on reducing shear forces and avoiding damage to cells. Specially designed agitator blades, such as propeller stirrers, are often used, and mild ventilation methods such as diffusion infiltration are also commonly employed.
Plant cell reactor: It is necessary to consider providing suitable oxygen transfer while ensuring good fluidity and low shear force. Improved stirred reactors or non stirred bubble and gas lift reactors can be used.
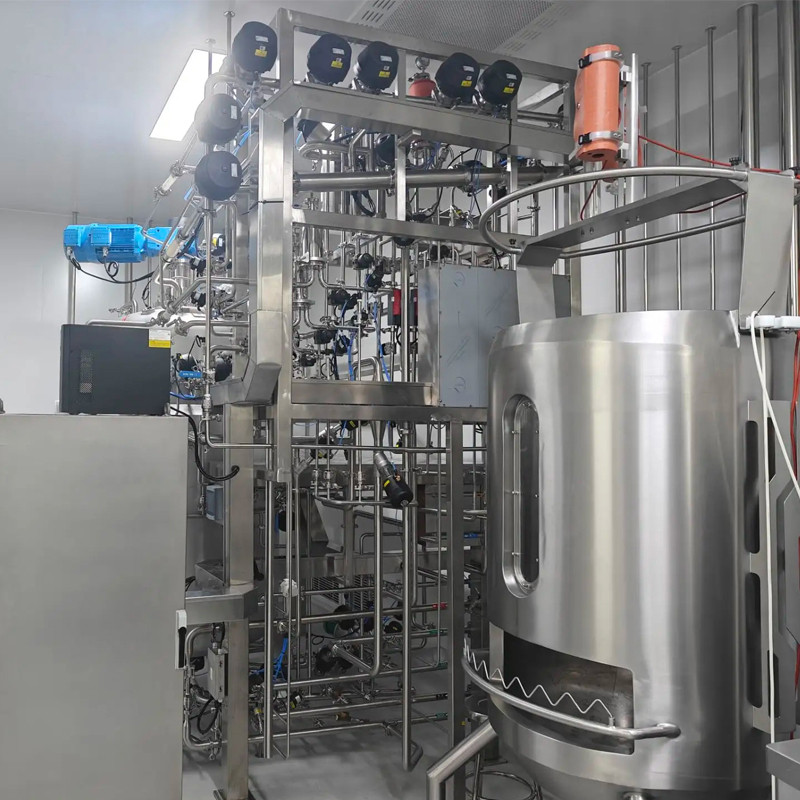

Cultivation process control
Microbial cells: grow and reproduce rapidly, with a short doubling time, usually 0.5-2 hours. During the fermentation process, it is necessary to focus on controlling the temperature pH、 Parameters such as dissolved oxygen and nutrient concentration are used to prevent contamination by miscellaneous bacteria.
Animal cells: grow slowly, with a typical doubling time of 12-60 hours. Need for stricter temperature control pH、 Environmental conditions such as dissolved oxygen and osmotic pressure, as well as prevention of cell apoptosis and differentiation.
Plant cells: grow slower than microorganisms and slightly faster than animal cells, with a typical doubling time of 24-72 hours. In addition to controlling temperature pH、 Dissolved oxygen, etc., also need to pay attention to light and the addition of plant hormones.
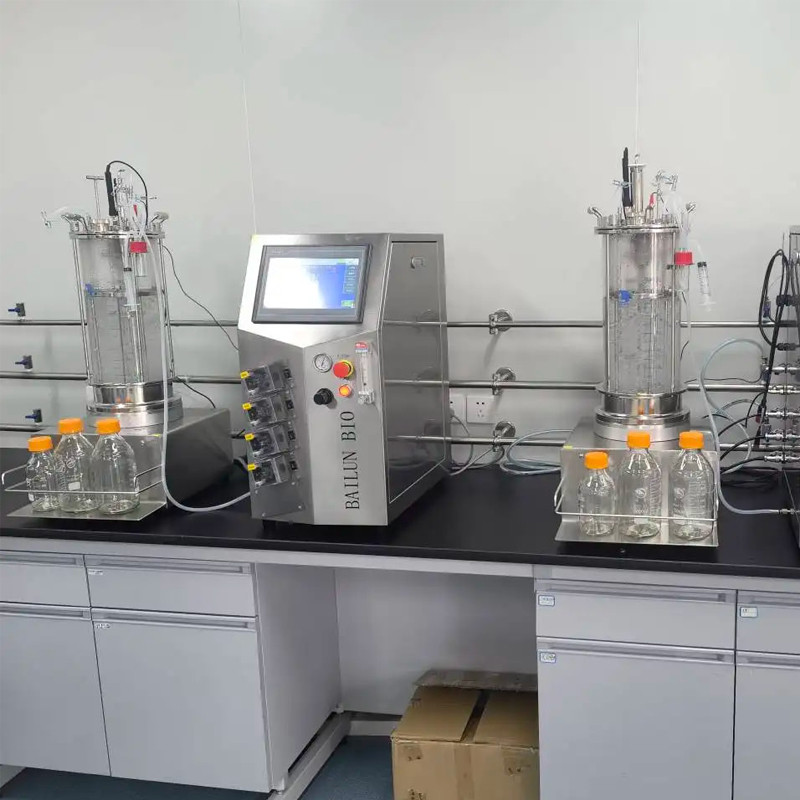

Application area
Microbial reactor: widely used in the fermentation industry, such as the production of antibiotics, amino acids, enzyme preparations, alcohol, beer, etc. It is also used in fields such as sewage treatment and bioenergy production.
Animal cell reactor: mainly used for the production of biological products such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, recombinant protein drugs, etc. It can also be used for cell therapy, tissue engineering and other research.
Plant cell reactor: It is used to produce plant secondary metabolites, such as plant saponins, essence, alkaloids, pharmaceutical proteins, etc. It can also be used for research on genetic transformation of plant cells and improvement of plant varieties.