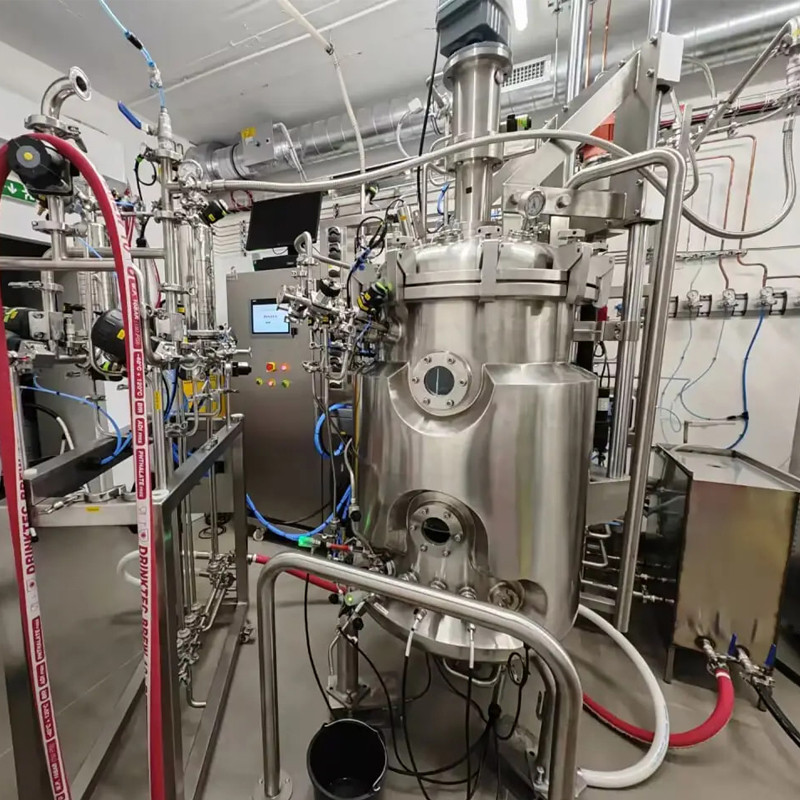
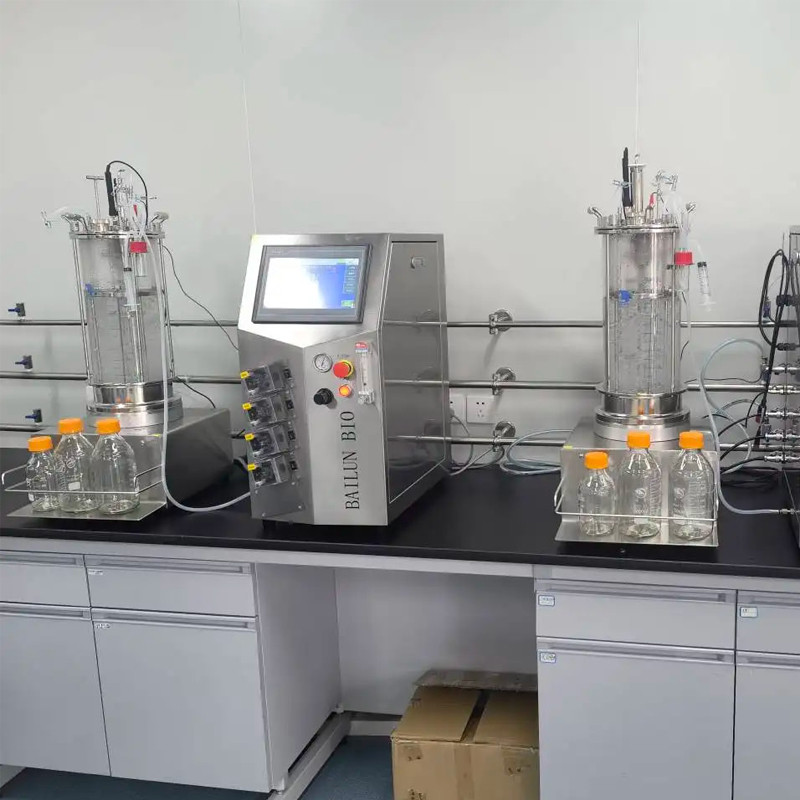
Pasteur Pichia pastoris is a type of methanol tolerant yeast that can utilize methanol as its sole carbon and energy source.
Like other yeasts, it mainly exists in haploid form during the asexual growth period. When the environment and nutrition are limited, it often induces two different physiological types of haploid cells to mate and fuse into a diploid form.
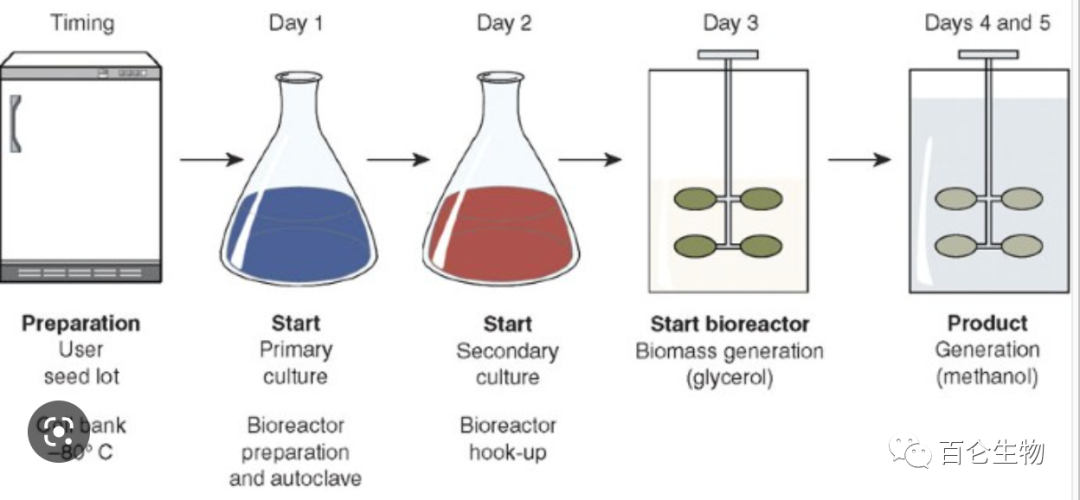
1、 Cell proliferation and reproduction during the production process of Pichia pastoris; Transition stage of batch feeding (glycerol or glucose); Induction expression stage (methanol);
The carbon source at each stage is a limiting matrix, and the dynamic model of its replenishment rate is the basis for efficient expression.
The advantages and disadvantages of Pichia pastoris are that it does not have natural plasmids in its body, so the expression vector needs to undergo homologous recombination with the host chromosome to integrate the exogenous gene expression framework into the chromosome for the expression of exogenous genes.
Including promoters, exogenous gene cloning sites, termination sequences, screening markers, etc.
The expression vectors are shuttle plasmids, which are first replicated and amplified in Escherichia coli, and then introduced into host yeast cells.
To induce extracellular secretion of the product, the expression vector also needs to carry a signal peptide sequence.
The advantages of Bailun fully automated laboratory reactor include the promoter of alcohol oxidase AOX1 gene, which is currently one of the strongest and most strictly regulated promoters;
The expression efficiency is high, and the exogenous proteins expressed can account for more than 90% of the total expressed proteins, which is beneficial for the separation and purification of the target protein; High density cultivation can be achieved in simple synthetic media;
The expression plasmid can stably integrate in the form of single or multiple copies at specific sites in the genome; Due to the fact that this yeast can use methanol as its sole carbon source and energy source, while the vast majority of microorganisms cannot use methanol as a carbon source, it can reduce pollution.
Insufficient fermentation cycle; Methanol is flammable, explosive, and toxic, posing a certain level of danger; The drugs required for screening high-yield strains are relatively expensive; The culture medium and conditions are not mature.

3、 Generally speaking, the influencing factors of Pichia pastoris fermentation include glucose concentration, temperature pH、 The concentrations of dissolved oxygen, nitrogen sources, nutrients, and bacterial cells themselves.
1. Except for a few special strains, the vast majority of yeast are usually suitable for growth at 20-25 ° C. In addition, higher temperatures are more advantageous for avoiding bacterial contamination.
The optimal fermentation temperature for Pichia pastoris is 30 ° C, and the growth temperature is 25-30 ° C. Fermentation in industry is generally controlled within the range of 30-35 ° C, within which yeast can grow and reproduce normally.
Once the temperature exceeds this range, enzymes quickly become inactive as the temperature increases, making yeast cells prone to aging and shortening the fermentation cycle, thereby affecting the expression of the target protein.
2. Pichia pastoris cells can adapt to a wide range of pH environments and grow in pH 2.0~7.5. The pH range of adaptation varies depending on the type of protein, and different proteins have different tolerances to different proteases. Choosing an appropriate pH can promote cell growth while avoiding a decrease in protease activity and preventing degradation of the target protein.
In industrial production, the pH is generally controlled between 4.5 and 5.5. During the fermentation process, the method of adding ammonia water online is often used to adjust the pH of the fermentation broth.
At the same time, ammonia water can also serve as a nitrogen source during the fermentation process, allowing the bacterial cells to grow rapidly and ultimately achieving complete expression of the target product.
3. The glucose concentration experiment has shown that the yield of bacterial cells gradually decreases when the initial glucose concentration is above 25g/L, indicating that higher glucose concentrations have a greater inhibitory effect on bacterial growth.
The growth rate of Pichia pastoris is higher at an initial glucose concentration of around 20g/L.
4. Dissolved oxygen Pichia pastoris is an aerobic microorganism, and its growth and metabolism require the participation of oxygen. Dissolved oxygen is one of the most important detection indicators during yeast cell growth.
Keeping DO at a low level indicates that the bacterial cells are consuming the carbon source in the fermentation broth. A rebound in DO indicates that the carbon source is depleted, and the bacterial cells are in a state of hunger, requiring timely supplementation of carbon source.
When oxygen is insufficient, the growth of bacterial cells will be limited. When DO is too high, the high concentration of oxygen free radicals in the fermentation broth will cause bacterial cell poisoning and death.
During the fermentation process, dissolved oxygen is generally controlled at 30%, while it is maintained at 20% during the induction stage.
5. By changing the initial yeast cell concentration, the fermentation performance of Pichia pastoris was evaluated, and it was found that the initial cell concentration had a significant impact on the fermentation performance of Pichia pastoris.
When the initial cell concentration is low, the cell growth rate is faster and protein expression is lower;
When the initial cell concentration is high, the substrate utilization rate slows down, and the protein concentration and yield are higher, because yeast cells use substrates to express proteins rather than for cell growth.
During the methanol induction stage, try to increase the concentration of bacterial cells as much as possible before induction to adapt to the methanol environment and reduce poisoning. At present, methanol induction is usually stopped when the wet weight reaches 180-220g/L.
6. In nitrogen source industrial production, organic nitrogen sources such as peptone are still used as nitrogen sources in seed culture media. During the fermentation process, a large amount of ammonia water is added to adjust the pH value, which also provides a nitrogen source for yeast cell growth.
7. The essential nutrients for inorganic salt Pichia pastoris include CaCl2, MgSO4, K2SO4, KH2PO4, and K2HPO4. Trace elements such as zinc, cobalt, manganese, molybdenum, copper, iron, etc. are also essential for yeast cells.
Some of them are cofactors of enzymes, while others are activators of enzymes. At low concentrations, these trace elements promote yeast growth and product synthesis, while at high concentrations, they can cause yeast poisoning and exhibit inhibitory effects.