The Economics and Applications of 5000-Liter Fermenters and Bioreactors: Insights into Prices and Biofermentation
In the world of biotechnology and industrial processes, 5000-liter fermenters and bioreactors play a crucial role. These large-scale vessels are not only essential for the production of various biological products but also have a significant impact on the economics and efficiency of the entire operation. This article aims to explore the diverse aspects related to 5000-liter fermenters and bioreactors, including their prices, functionality, and the role of biofermentators in different industries.
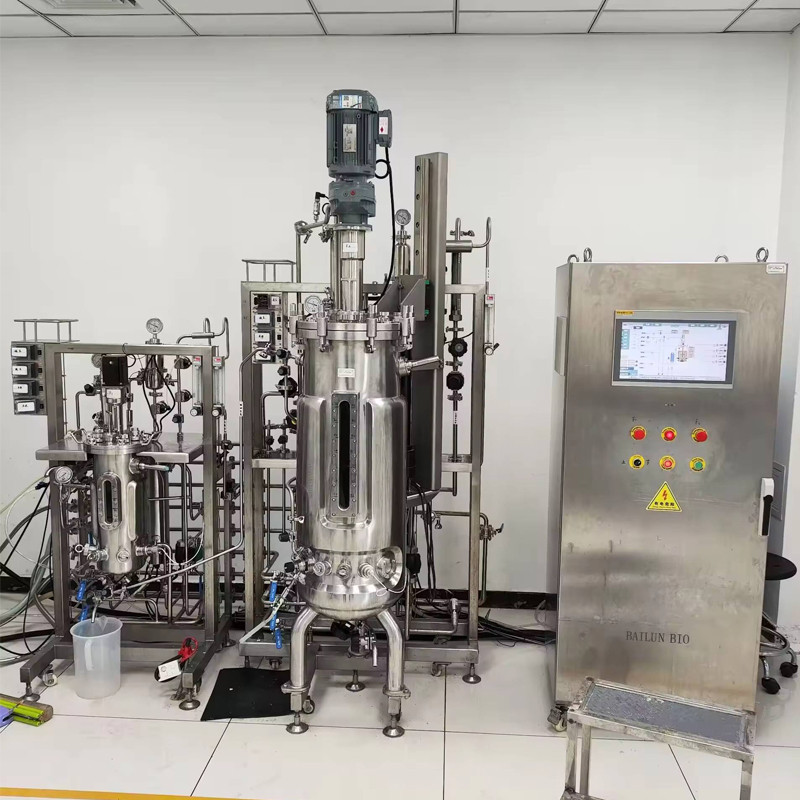
The price of a 5000-liter fermenter or bioreactor can vary significantly depending on several factors. The materials used in its construction are of paramount importance. High-quality stainless steel, for instance, is often preferred for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning and sterilization. However, this choice comes at a cost. The more advanced the grade of stainless steel, the higher the price.
The complexity and sophistication of the control systems also contribute to the overall cost. State-of-the-art sensors for monitoring parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and pressure, along with precise control mechanisms for regulating these variables, add to the expense. Additionally, features like automated sampling systems, data logging capabilities, and remote monitoring interfaces increase the functionality but also the price tag.
The design and engineering of the Stainless Steel fermenter or bioreactor can have a substantial impact on its cost. Specialized agitator designs, optimized heat exchange systems, and efficient aeration mechanisms require in-depth research and development, which is reflected in the price. Customization options to meet specific process requirements or industry standards can further drive up the cost.

Brand reputation and the manufacturer's experience and expertise also play a role in pricing. Established manufacturers with a proven track record of delivering reliable and high-performance equipment often command higher prices compared to lesser-known or new entrants in the market.
When considering the price of a 5000-liter fermenter or bioreactor, it's essential to look beyond the initial purchase cost and take into account the total cost of ownership over its lifespan. Maintenance and repair costs, energy consumption, and the cost of spare parts and consumables can add up significantly over time.
Biofermentators, in the context of 5000-liter systems, offer numerous advantages in various applications. In the pharmaceutical industry, they are used for the production of antibiotics, vaccines, and therapeutic proteins. The large volume allows for economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit of the final product. The controlled environment within the biofermentator ensures consistent quality and purity, which is critical for meeting strict regulatory standards.
In the food and beverage sector, 5000-liter biofermentators are employed in the production of beverages like beer and wine, as well as the manufacture of enzymes and food additives. The ability to precisely control the fermentation process leads to products with desired flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles.
The biotechnology field benefits from these systems in the development of biofuels and the production of specialty chemicals. Microbial fermentation in 5000-liter biofermentators can convert biomass into sustainable energy sources or produce valuable compounds for various industrial applications.
The operation of a 5000-liter fermenter or Cell Culture bioreactor requires a skilled and trained workforce. Operators need to have a deep understanding of the biological processes, as well as the technical aspects of the equipment. This includes knowledge of how to set and adjust parameters, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the smooth running of the fermentation process.
The choice of a 5000-liter fermenter or bioreactor depends on several factors, including the type and scale of the production process, the nature of the microorganisms or cells being cultivated, and the available infrastructure and budget. Smaller companies or research institutions might opt for shared or leased facilities to access this level of equipment without the hefty upfront investment.

Looking to the future, advancements in technology are likely to drive down the costs of 5000-liter fermenters and bioreactors while improving their performance and efficiency. New materials and manufacturing techniques could make the equipment more affordable and durable. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in control systems could optimize the fermentation process, reducing waste and increasing productivity.
In conclusion, 5000-liter fermenters and bioreactors are vital assets in modern biotechnology and industrial processes. Understanding the factors influencing their prices and the diverse applications of biofermentators is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing the benefits they offer. As technology continues to evolve, these systems are likely to play an even more significant role in driving innovation and economic growth in various sectors.